The HTML5 Canvas API is a powerful tool that allows developers to draw graphics, shapes, and images directly in a web browser using JavaScript. Among its many features, drawing images onto the canvas is one of the most exciting because it opens up creative possibilities, such as creating games, dynamic visualizations, and photo editing tools. The ability to draw images dynamically means you can manipulate pictures in real-time, applying transformations like resizing, cropping, or animating with ease.

with hands-on learning.
get the skills and confidence to land your next move.
At the heart of drawing images on canvas is the drawImage method. This method is versatile and can handle different ways to render images: placing them at specific locations, resizing them, or even drawing a cropped section of an image. This article will walk you through how to use the canvas and drawImage method with real, engaging examples, helping you bring your ideas to life visually.
Setting Up Canvas and Loading an Image
Before we draw any images, we need a canvas element and a JavaScript environment to draw on it. The canvas provides a drawable region on your webpage. We then use JavaScript to grab the 2D rendering context, which gives us access to methods like drawImage. Loading images involves creating an Image object, setting its source, and waiting for the image to fully load before drawing it on the canvas.
Here’s a simple example where we load a playful cat image and draw it once it’s ready:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Basic Image Drawing on Canvas</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="myCanvas" width="400" height="300" style="border:1px solid black;"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('myCanvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const catImage = new Image();
catImage.src = 'https://cataas.com/cat?width=200&height=200'; // Fun cat image
catImage.onload = function() {
ctx.drawImage(catImage, 50, 50);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>In this code, we first create a canvas of 400 by 300 pixels and grab its 2D context. Then, we create a new Image object and set its source to a cat picture from cataas.com. The onload event ensures the image is fully loaded before attempting to draw it. When ready, drawImage places the cat at coordinates (50, 50) on the canvas.
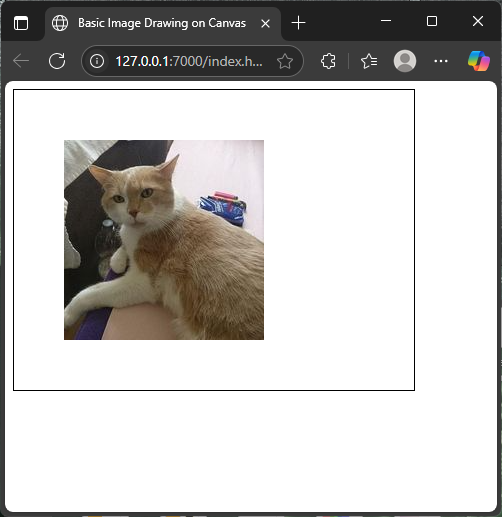
Drawing an Image at Specific Coordinates
The most basic use of drawImage involves specifying the image and where on the canvas it should appear. The x and y coordinates determine the top-left corner position of the image. This lets you control exactly where images are placed, enabling the creation of fun layouts or collages.
Here’s an example where we draw the same cat image multiple times at different positions:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Drawing Images at Different Coordinates</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="500" height="350" style="border:1px solid gray;"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const cat = new Image();
cat.src = 'https://cataas.com/cat?width=100&height=100';
cat.onload = function() {
ctx.drawImage(cat, 20, 20);
ctx.drawImage(cat, 150, 20);
ctx.drawImage(cat, 280, 20);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>This code places three copies of the cat image spaced evenly across the top part of the canvas. Each call to drawImage uses different x coordinates (20, 150, 280) but the same y coordinate (20). This allows for easy positioning of images for playful effects.
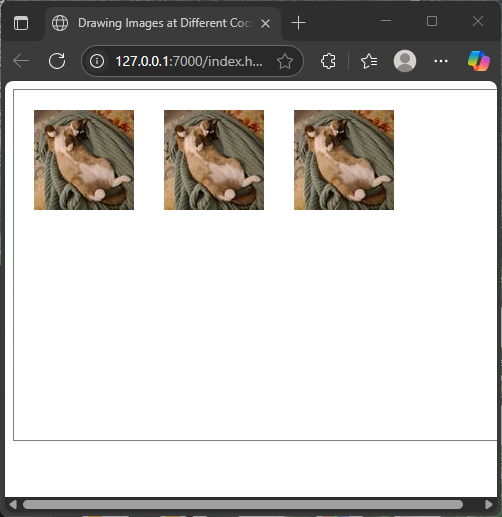
Scaling Images on Canvas
Besides placing images, you can resize them as you draw. The drawImage method accepts width and height parameters after the x and y coordinates, allowing you to scale images larger or smaller on the fly. This is useful for emphasizing or shrinking images without editing the source file.
The following example demonstrates drawing a dog image first at its normal size and then scaled up and down:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Scaling Images on Canvas</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="scalingCanvas" width="600" height="300" style="border:1px solid #333;"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('scalingCanvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const dog = new Image();
dog.src = 'https://placedog.net/150/150';
dog.onload = function() {
// Draw original size
ctx.drawImage(dog, 20, 20);
// Draw scaled smaller
ctx.drawImage(dog, 200, 20, 75, 75);
// Draw scaled larger
ctx.drawImage(dog, 350, 20, 225, 225);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>In this code, we draw the dog image three times. The first drawing uses the natural image size. The second drawing shrinks it to 75×75 pixels. The third enlarges it to 225×225 pixels. This shows how width and height parameters let you manipulate image size dynamically.
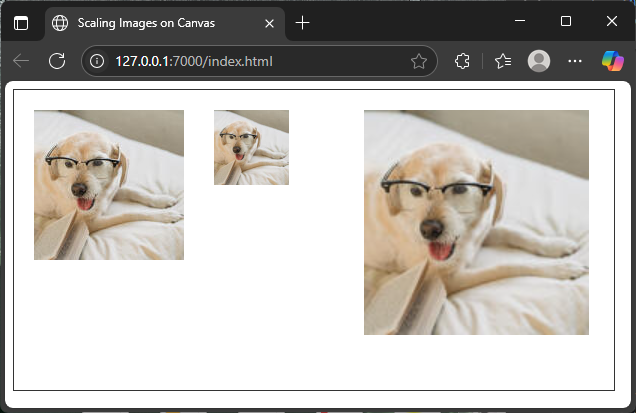
Cropping and Drawing Part of an Image
You can also draw only a part of an image by defining a source rectangle inside the image and a destination rectangle on the canvas. This advanced drawImage syntax takes eight parameters: the coordinates and size of the source rectangle (sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight) and the coordinates and size of the destination rectangle (dx, dy, dWidth, dHeight). This cropping is useful for sprite sheets or focusing on specific image parts.
Here’s a lively example that crops and draws just the face of a cat multiple times:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Cropping Part of an Image</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="cropCanvas" width="400" height="300" style="border:1px solid #666;"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('cropCanvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const catFull = new Image();
catFull.src = 'https://cataas.com/cat?width=400&height=300';
catFull.onload = function() {
// Crop rectangle: top-left 100x100 pixels of image (cat's face)
const sx = 100;
const sy = 50;
const sWidth = 100;
const sHeight = 100;
// Draw cropped face multiple times at different canvas spots
ctx.drawImage(catFull, sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, 20, 20, 100, 100);
ctx.drawImage(catFull, sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, 150, 20, 150, 150);
ctx.drawImage(catFull, sx, sy, sWidth, sHeight, 320, 20, 60, 60);
};
</script>
</body>
</html>This example loads a larger cat image and draws just a cropped 100×100 section, which represents the cat’s face, in three different sizes and positions on the canvas. The cropping coordinates let us isolate just the desired portion.
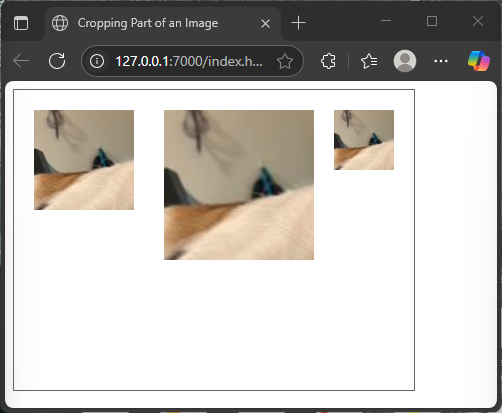
Drawing Multiple Images with Animations
The canvas API allows you to draw many images and refresh the drawing to create animation. By clearing and redrawing images at new positions in a loop, you can simulate motion. While animation is beyond the main scope, here’s a simple, fun example of a spaceship gliding across the screen.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Animating Images on Canvas</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="animCanvas" width="600" height="400" style="border:1px solid black;"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('animCanvas');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const spaceship = new Image();
spaceship.src = 'https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/41/Space_Shuttle_Columbia_launching.jpg/250px-Space_Shuttle_Columbia_launching.jpg';
let xPos = 0;
spaceship.onload = function() {
function animate() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
ctx.drawImage(spaceship, xPos, 50, 250, 250);
xPos += 2;
if (xPos > canvas.width) xPos = -100; // Reset to start off-canvas
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
animate();
};
</script>
</body>
</html>Here, we load a spaceship image and move it horizontally by increasing the x position each frame. The clearRect method clears the canvas before redrawing. This creates a smooth animation of the spaceship traveling from left to right.
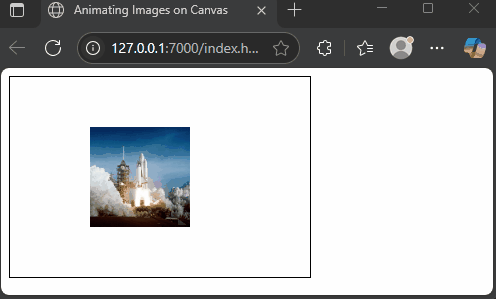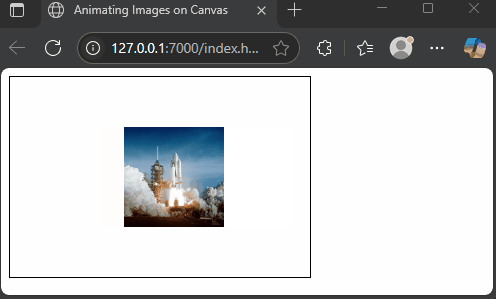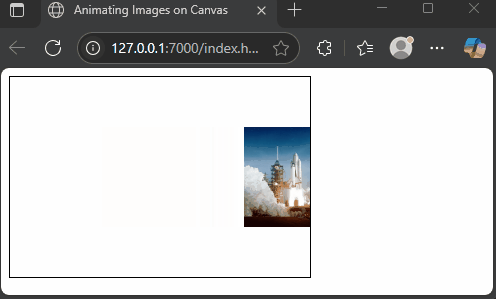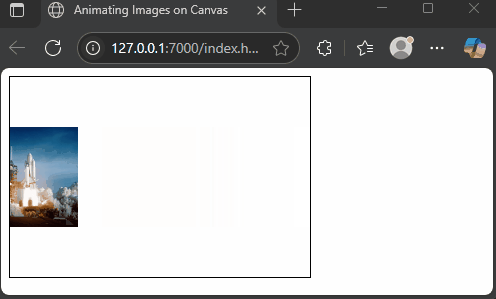
Conclusion
Drawing images on the JavaScript canvas unlocks a world of visual creativity. From simply placing pictures at specific coordinates to resizing and cropping them, you have many ways to control how images appear on your webpage. The drawImage method is versatile, letting you bring photos, artwork, or sprites into your canvas projects with precision.
This guide showed you how to set up the canvas, load images, draw them in various ways, and even add simple animation. By experimenting with these techniques, you can build anything from playful collages to interactive games that come alive on the canvas.
References
- MDN Web Docs: CanvasRenderingContext2D.drawImage()
- MDN Web Docs: Canvas API
- HTML Living Standard: Canvas element







