Colors play a crucial role in any form of visual art, including web graphics. In the context of the HTML5 Canvas API, colors breathe life into shapes, text, and images, turning simple outlines into vibrant and engaging visuals. Using colors effectively in canvas not only improves aesthetics but also helps convey meaning, mood, and style. Whether you’re drawing a sunny landscape or a dynamic game interface, understanding how to work with colors is fundamental.

with hands-on learning.
get the skills and confidence to land your next move.
Beyond solid colors, gradients allow for smooth color transitions, adding depth and dimension that flat colors cannot achieve. Gradients are blends of two or more colors that gradually shift along a line or radiate from a point. They are perfect for creating natural effects like shadows, highlights, or glowing light. This article will guide you through how to use solid colors and gradients on the canvas with clear, fun, and practical examples.
Setting the Fill and Stroke Colors
Before diving into gradients, it’s important to understand the basics of how colors work in canvas. The canvas rendering context has two key properties: fillStyle and strokeStyle. These control the colors used when filling shapes and drawing outlines, respectively.
You can assign these properties solid colors by using color names like "red", hexadecimal color codes like "#FF5733", or RGB strings like "rgb(255,0,0)".
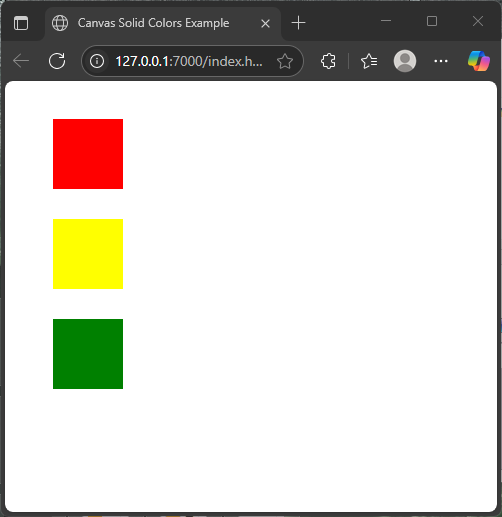
Here is an example that draws a simple traffic light using solid rectangles filled with red, yellow, and green:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas Solid Colors Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="trafficLight" width="150" height="400"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('trafficLight');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Draw the red light
ctx.fillStyle = 'red';
ctx.fillRect(40, 30, 70, 70);
// Draw the yellow light
ctx.fillStyle = '#FFFF00'; // Hex code for yellow
ctx.fillRect(40, 130, 70, 70);
// Draw the green light
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgb(0,128,0)'; // RGB for green
ctx.fillRect(40, 230, 70, 70);
</script>
</body>
</html>This code creates three filled rectangles stacked vertically, each with a different color. The fillStyle is set before each shape is drawn, determining the color used for that shape’s fill. This basic method forms the foundation for all canvas coloring.
Using RGBA Colors for Transparency
Sometimes, you want shapes to be partially transparent so that they can overlap with a see-through effect. This is where the RGBA color format shines. It adds an alpha channel for opacity (from 0 fully transparent to 1 fully opaque).
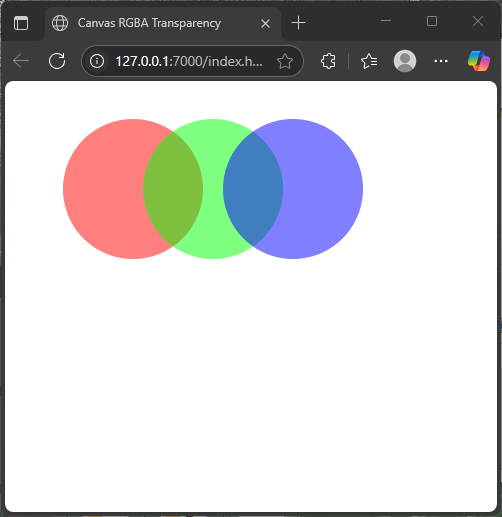
Here’s an example drawing overlapping semi-transparent circles using rgba() colors:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas RGBA Transparency</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="venn" width="400" height="200"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('venn');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Draw a semi-transparent red circle
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5)';
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(120, 100, 70, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fill();
// Draw a semi-transparent green circle overlapping the red
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0, 255, 0, 0.5)';
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(200, 100, 70, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fill();
// Draw a semi-transparent blue circle overlapping the red and green
ctx.fillStyle = 'rgba(0, 0, 255, 0.5)';
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(280, 100, 70, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fill();
</script>
</body>
</html>In this example, three colorful circles overlap, showing how transparent fills combine visually. The alpha value 0.5 makes each circle half see-through, creating a fun, layered Venn diagram effect.
Creating Linear Gradients
A linear gradient is a color transition along a straight line. You create one in canvas by calling createLinearGradient(x0, y0, x1, y1) where (x0, y0) and (x1, y1) define the start and end points of the gradient line.
After creating the gradient object, you add colors at different positions using addColorStop(offset, color). The offset is a value from 0 (start) to 1 (end) that sets where the color appears.
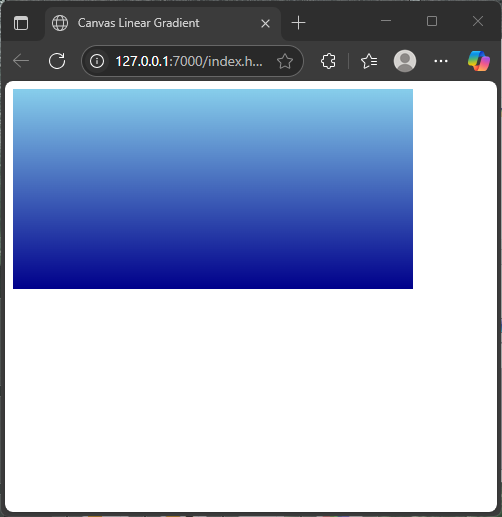
This example paints a sky with a vertical gradient from light blue at the top to dark blue at the bottom:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas Linear Gradient</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="sky" width="400" height="200"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('sky');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Create a vertical linear gradient
const gradient = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 0, 200);
gradient.addColorStop(0, '#87CEEB'); // Light sky blue
gradient.addColorStop(1, '#00008B'); // Dark blue
// Use the gradient as fill style
ctx.fillStyle = gradient;
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, 400, 200);
</script>
</body>
</html>Here, the fillRect fills the entire canvas with the gradient, smoothly blending from light to dark blue. This effect mimics a natural sky fading toward the horizon.
Creating Radial Gradients
Radial gradients spread colors in circles radiating from a center point outward. Use createRadialGradient(x0, y0, r0, x1, y1, r1) where (x0, y0, r0) defines the start circle and (x1, y1, r1) defines the end circle.
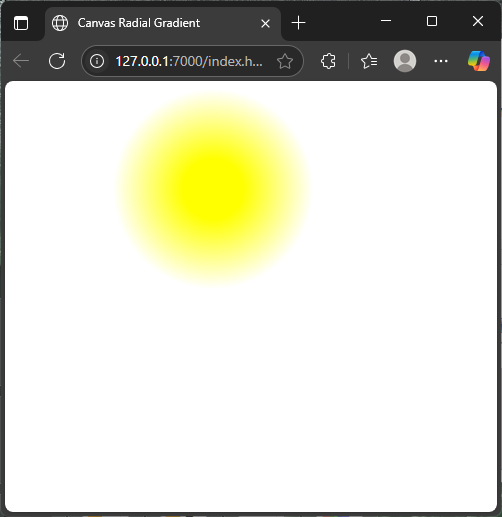
This example draws a glowing sun using a radial gradient that fades from bright yellow in the center to transparent:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas Radial Gradient</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="sun" width="400" height="200"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('sun');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Create a radial gradient centered at (200, 100)
const gradient = ctx.createRadialGradient(200, 100, 30, 200, 100, 100);
gradient.addColorStop(0, 'yellow');
gradient.addColorStop(1, 'rgba(255, 255, 0, 0)'); // Transparent yellow
// Fill a circle with the radial gradient
ctx.fillStyle = gradient;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(200, 100, 100, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fill();
</script>
</body>
</html>The glow effect comes from the gradient’s center being solid yellow and fading smoothly to fully transparent on the edges.
Applying Gradients to Shapes
Both linear and radial gradients can be assigned to fillStyle or strokeStyle to fill or outline shapes. This flexibility allows creating rich effects.
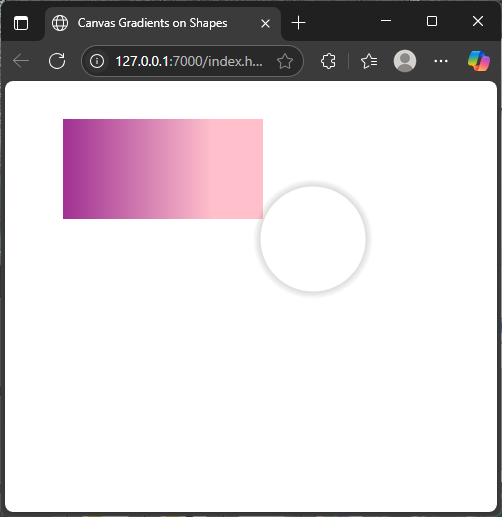
For example, here is a rectangle filled with a horizontal linear gradient, and a circle outlined with a radial gradient stroke:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas Gradients on Shapes</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="gradShapes" width="400" height="250"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('gradShapes');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Linear gradient for rectangle fill
const linGrad = ctx.createLinearGradient(0, 0, 200, 0);
linGrad.addColorStop(0, 'purple');
linGrad.addColorStop(1, 'pink');
ctx.fillStyle = linGrad;
ctx.fillRect(50, 30, 200, 100);
// Radial gradient for circle stroke
const radGrad = ctx.createRadialGradient(300, 150, 10, 300, 150, 60);
radGrad.addColorStop(0, 'orange');
radGrad.addColorStop(1, 'transparent');
ctx.lineWidth = 15;
ctx.strokeStyle = radGrad;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(300, 150, 60, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.stroke();
</script>
</body>
</html>This example showcases how combining different gradients and shapes can create dynamic visuals. The rectangle smoothly shifts color horizontally, while the circle glows softly around its edge.
Combining Solid Colors and Gradients
You can mix solid colors with gradients to create more complex effects. For instance, you can fill stripes with solid colors and outline them with a gradient stroke, giving a fun and festive look.
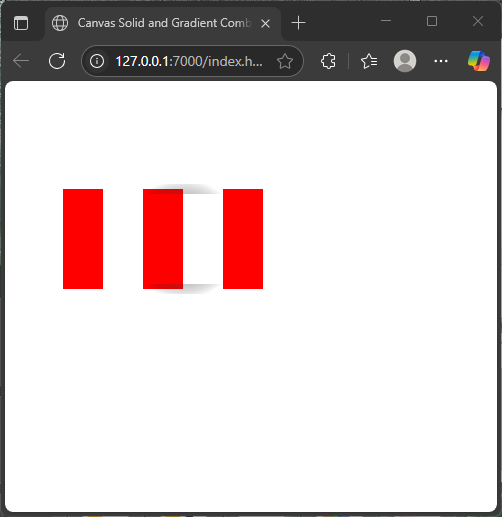
Here is a playful candy cane with solid white and red stripes and a gradient stroke for a shiny effect:
<html>
<head>
<title>Canvas Solid and Gradient Combination</title>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="candyCane" width="400" height="300"></canvas>
<script>
const canvas = document.getElementById('candyCane');
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
// Draw solid stripes - alternating red and white
const stripeWidth = 40;
for(let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
ctx.fillStyle = (i % 2 === 0) ? 'red' : 'white';
ctx.fillRect(50 + i * stripeWidth, 100, stripeWidth, 100);
}
// Create a radial gradient for shiny stroke effect
const gradientStroke = ctx.createRadialGradient(170, 150, 10, 170, 150, 60);
gradientStroke.addColorStop(0, 'pink');
gradientStroke.addColorStop(1, 'transparent');
ctx.lineWidth = 10;
ctx.strokeStyle = gradientStroke;
ctx.strokeRect(50, 100, stripeWidth * 6, 100);
</script>
</body>
</html>In this example, the solid red and white stripes form the candy cane body, while the gradient stroke adds a soft, glowing outline, making the shape pop visually. This shows how gradients can complement solid colors for engaging effects.
Conclusion
Working with colors and gradients in the JavaScript canvas is a powerful way to bring your graphics to life. Starting with basic solid colors using fillStyle and strokeStyle gives you control over fills and outlines. Expanding into RGBA colors adds transparency, which opens up creative overlapping possibilities.
Linear and radial gradients add depth and smooth color transitions, perfect for natural scenes, glowing effects, or rich designs. Applying gradients to fills and strokes offers endless possibilities for creative visuals. Combining solid colors with gradients further enhances the artistic potential of canvas drawings.
By mastering these how-tos, you are equipped to create colorful, vibrant, and dynamic canvas art that engages and delights. Experimenting with these techniques will let your creativity run wild with color.
References
- MDN Web Docs – CanvasRenderingContext2D.fillStyle
- MDN Web Docs – CanvasRenderingContext2D.createLinearGradient()
- MDN Web Docs – CanvasRenderingContext2D.createRadialGradient()
- MDN Web Docs – Canvas API







